Click on the image to load it in its full size
Figure 8 - Haidurov A, Budanov AV: Locked in Structure: Sestrin and GATOR–A Billion-Year Marriage. Cells 2024, 13
The hypothetical journey of Sestrin evolution. On the left, AhpD from Streptococcus pnemoniae, considered a homolog of Sestrins' SESN-A domain. On the right - human SESN2. In between, various structural homologues found using AlphaFold Foldseek by Martin Steinegger lab.
Sestrin could be a fused chain of duplicated AhpD proteins, in which one AhpD domain was free to evolve a concordant function to the anti-oxidative function of AhpD.
Figure 2 - Haidurov A, Budanov A.V: Sestrins in Carcinogenesis—The Firefighters That Sometimes Stoke the Fire. Cancers 2025, 17:1578.
Stress-induced upregulation of Sestrin genes and the associated transcription factors mediating this response.
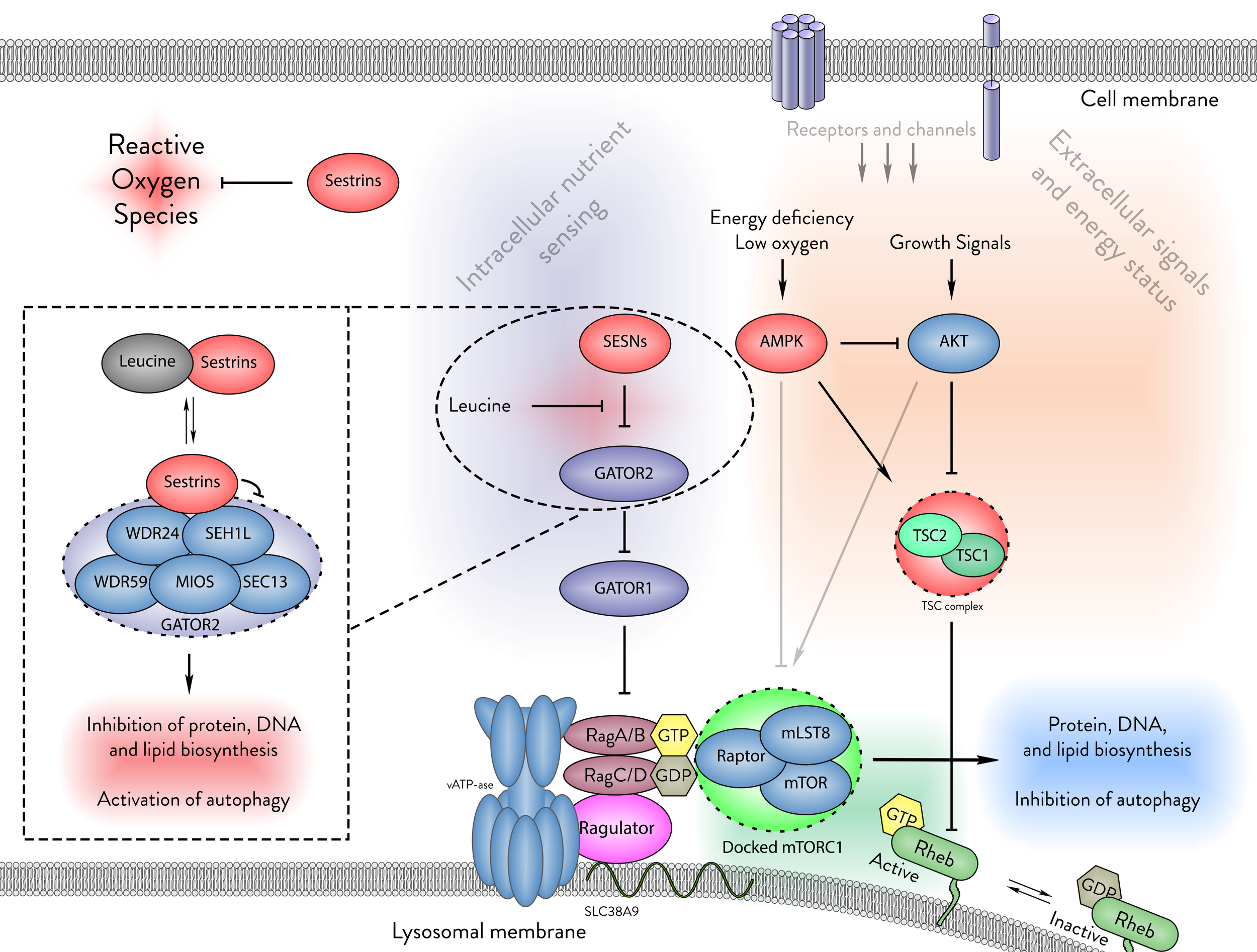
Figure 1 - Haidurov A, Budanov AV: Locked in Structure: Sestrin and GATOR–A Billion-Year Marriage. Cells 2024, 13
Stress-induced upregulation of Sestrin genes and the associated transcription factors mediating this response.
Figure 1 - Haidurov A: p53-regulated SESN1 and SESN2 regulate cell proliferation and cell death through control of STAT3. PhD Thesis, University of Dublin, 2024.
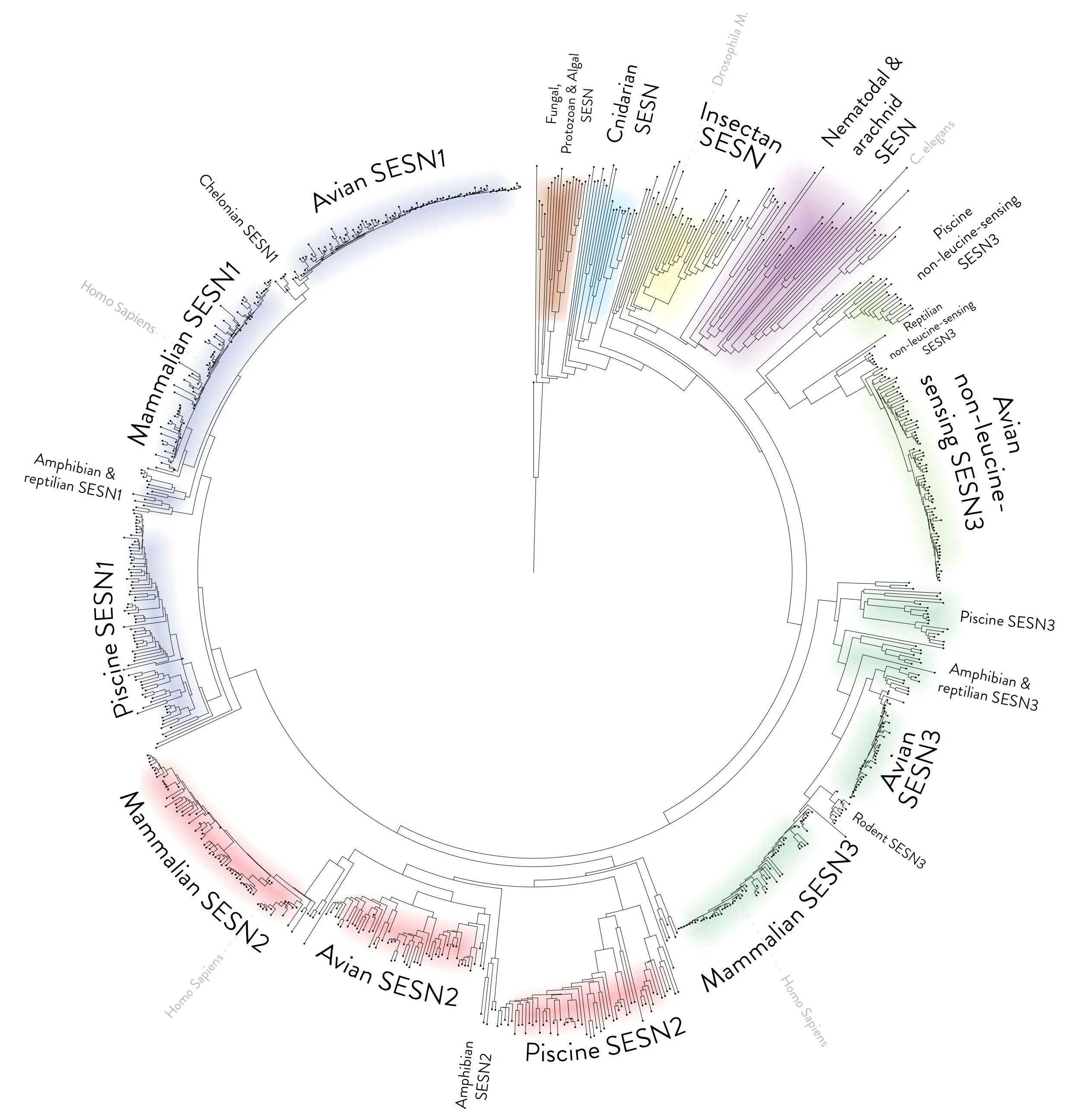
A circular phylogenetic tree based on protein alignments of Sestrin. The tree displays 805 Sestrin and Sestrin-like proteins as nodes at the tip of a leaf. Protein BLAST was used to select species with homologous proteins to the C. Elegans Sestrin sequence. One species of every genus was selected manually via BLAST's taxonomic display, and FASTA sequences were retrieved for each protein. A multiple sequence alignment was performed using EMBL-EBI Clustal Omega. The programme was used to export the alignment as a Newick format phylogenetic tree. The file was imported into the Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) programme, and the tool was used to root the tree on the sequence of Naegleria gruberi, and some visual aspects of the tree were adjusted. The figure of the circular tree was exported as an image file. The tree was then annotated and coloured manually using Adobe Photoshop. As this is a protein-aligned phylogenetic tree, the distances on the tree are arbitrary. The distance from a node to the tip of a leaf represents the difference in the sequence from a previous assumed ancestor protein.
Figure 2 - Haidurov A, Budanov AV: Locked in Structure: Sestrin and GATOR–A Billion-Year Marriage. Cells 2024, 13
The hypothetical journey of Sestrin evolution. On the left, AhpD from Streptococcus pnemoniae, considered a homolog of Sestrins' SESN-A domain. On the right - human SESN2. In between, various structural homologues found using AlphaFold Foldseek by Martin Steinegger lab.
Sestrin could be a fused chain of duplicated AhpD proteins, in which one AhpD domain was free to evolve a concordant function to the anti-oxidative function of AhpD.
Figure 7 - Haidurov A, Budanov AV: Locked in Structure: Sestrin and GATOR–A Billion-Year Marriage. Cells 2024, 13
The hypothetical journey of Sestrin evolution. On the left, AhpD from Streptococcus pnemoniae, considered a homolog of Sestrins' SESN-A domain. On the right - human SESN2. In between, various structural homologues found using AlphaFold Foldseek by Martin Steinegger lab.
Sestrin could be a fused chain of duplicated AhpD proteins, in which one AhpD domain was free to evolve a concordant function to the anti-oxidative function of AhpD.